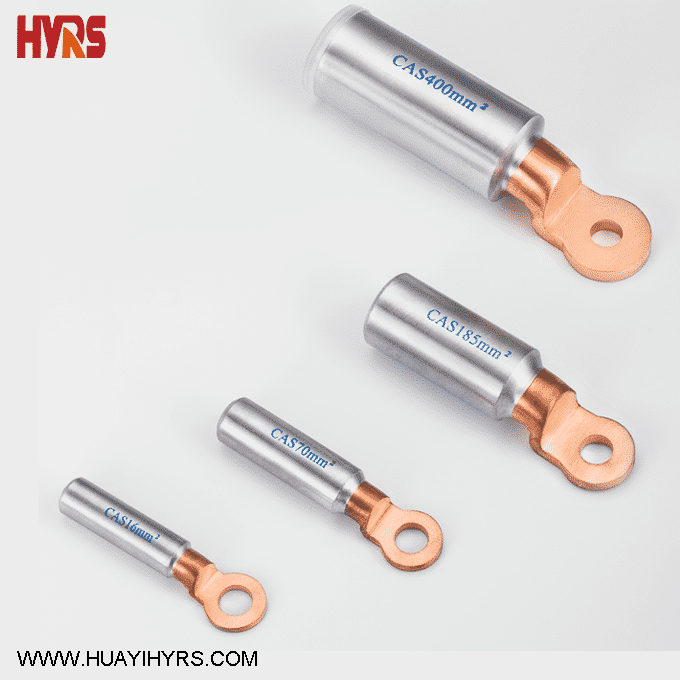
Cable is one of the indispensable electrical equipment in our daily life, widely used in power, communication, transportationand other fields. The basic structure of the cable includes the core, insulation layer, protective layer and other parts, of whichthe core is the core part of the cable, which plays the role of transmitting electrical energy or signals.
1.The role and type of Wire Core
The core is the central part of the cable and is the transmission path of the current or signal. The wire core is made of metalmaterials, common copper, aluminum, aluminum alloy and so on. According to different uses, the wire core can be dividedinto power wire core and signal wire core.
a.Cable Core
Power line core is used to transmit electrical energy, according to the current frequency and voltage of the different, power line core can be divided into the following types:
(1) High-voltage power line core: suitable for high-voltage transmission lines, generally using steel wire or aluminum wire as the skeleton, the outside wrapped insulation layer.
(2) Low-voltage power line core: suitable for low-voltage distribution lines, generally using multiple strands of copper wire or aluminum wire as a conductor, wrapped in insulation layer.
(3) Communication power line core: suitable for communication power lines, generally using multiple strands of copper wire or aluminum wire as a conductor, wrapped in insulation layer.
b. Signal Cable Core
Signal core is used to transmit signals, according to the different transmission signals, signal core can be divided into the following types:
(1) Telephone line core: suitable for telephone communication lines, generally using multiple strands of copper wire or aluminum wire as a conductor, wrapped in insulation layer.
(2) Network wire core: suitable for computer network lines, generally using multiple strands of copper wire or aluminum wire as a conductor, the external insulation layer is wrapped.
(3) Video wire core: suitable for video transmission lines, generally using multiple strands of copper wire or aluminum wire as a conductor, the outside of the insulation layer.
2.Manufacturing process of wire core
The manufacturing process of wire core mainly includes drawing, stranding, insulating layer wrapping and other steps. The following takes copper wire as an example to briefly introduce the manufacturing process of wire core.
a. Wire drawing
Wire drawing is the process of gradually drawing copper ingots into fine wires through a series of dies. In the wire drawing process, the copper ingot is extruded and stretched by several molds, and gradually becomes a fine wire. Drawing requires precise control of mold temperature, pressure and lubricant use to ensure that the diameter and strength of the filaments meet the requirements.
b. Hinge
Stranding is the process of stranding multiple filaments in a certain direction and spacing into one strand. According to the different direction of the stranding, it can be divided into the same direction and two-way stranding. Homodirectional stranding means that the direction of stranding is the same, and bidirectional stranding means that the direction of stranding is opposite. The stranding process requires controlling the stranding speed and temperature to ensure the structure stability and beautiful appearance of the wire core.
c. Insulation Layer Wrap
The insulating layer wrapping is to wrap the insulating material on the stranded wire core to protect the wire core from the external environment. Commonly used insulation materials include polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene and so on. The wrapping process of the insulation layer requires that the wrapping speed and temperature be controlled to ensure that the thickness and uniformity of the insulation layer meet the requirements.
3.The Structural Parameters of the Wire Core
The structure parameter of the conductor core is an important index to measure the performance of the conductor core, including conductor cross-sectional area, conductor resistivity, insulating layer thickness, etc. The following describes the meanings and functions of these parameters.
a.Conductor Cross-sectional Area
The cross-sectional area of a conductor is the cross-sectional area of a metal conductor in a wire core, in square millimeters (mm2) . The cross-sectional area of the conductor determines the current that the conductor core can transmit. The larger the cross-sectional area, the larger the transmission current. When selecting cables, select the appropriate conductor cross-sectional area based on actual needs.
b.Conductor Resistivity
Conductor resistivity refers to the resistance of a metal conductor to an electric current and is expressed in ohms · meters (Ω·m). The smaller the conductor resistivity, the better the conductor conductivity. Common metal conductor materials include copper, aluminum, aluminum alloy, etc., of which copper has a low resistivity, so it is commonly used as a conductor material for power cables.


 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик