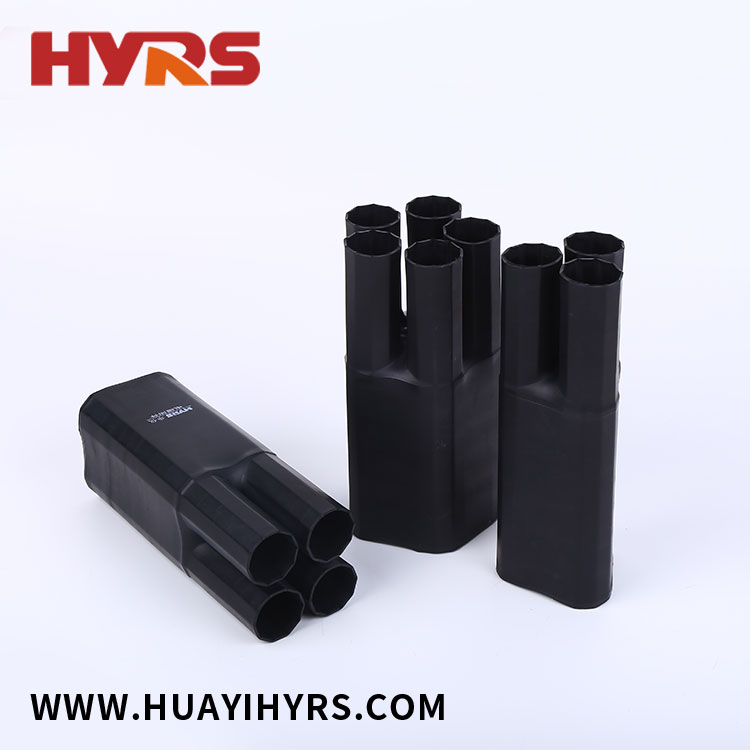
Heat shrinkable tube, a ubiquitous player in the world of electrical insulation and protection, comes in various materials, each boasting unique properties. But how durable are these tubes, and which ones excel in specific environments? Let's delve into the world of heat shrinkable tube and explore the factors that determine its resilience.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Material Matters
The durability of heat shrinkable tube hinges largely on the material it's composed of. Here's a breakdown of some common types and their key strengths:
Polyolefin (POF): The most widely used heat shrinkable tube material, POF offers a good balance of affordability and performance. It boasts excellent electrical insulation properties and is resistant to common chemicals like oils and greases. However, POF may not be ideal for extreme temperatures or highly corrosive environments.
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF): For superior durability, PVDF heat shrinkable tube steps up to the challenge. This champion stands out for its exceptional resistance to flame, harsh chemicals, and industrial fuels. Its robust construction makes it highly resistant to punctures and tears. PVDF is the ideal choice for applications demanding long-term performance in demanding environments.
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene (FEP): Offering a balance between POF and PVDF, FEP heat shrinkable tube provides excellent chemical resistance and good electrical insulation. It's known for its superior flexibility, even at low temperatures, making it suitable for applications requiring a wider range of motion.
Silicone: When flexibility and high-temperature resistance are paramount, silicone heat shrinkable tube reigns supreme. It remains flexible even at extreme cold temperatures and can withstand significantly higher temperatures compared to other materials. This makes silicone ideal for applications involving high heat, such as engine compartments or lighting fixtures.
Beyond Material: Additional Factors Affecting Durability
While material selection is crucial, other factors also influence the durability of heat shrinkable tube:
Wall Thickness: Thicker walled heat shrinkable tube offers greater mechanical strength and puncture resistance compared to thinner walled options. However, thicker walls require higher shrink ratios and may limit flexibility.
Shrink Ratio: The shrink ratio refers to the amount a heat shrinkable tube shrinks upon application of heat. A higher shrink ratio allows for greater versatility in accommodating various wire sizes but may also impact the overall durability of the shrunk tube.
Choosing the Right Heat Shrinkable Tube for Optimal Durability
Selecting the most durable heat shrinkable tube for your application requires considering the specific environmental demands:
For basic electrical insulation and protection in moderate environments, POF heat shrinkable tube offers a cost-effective solution.
In applications involving harsh chemicals, flames, or industrial fuels, PVDF heat shrinkable tube provides exceptional long-term durability.
For applications requiring flexibility and a wider range of temperatures, FEP heat shrinkable tube is a good choice.
When extreme high temperatures are a concern, silicone heat shrinkable tube offers unmatched heat resistance and flexibility.
Heat shrinkable tube offers a spectrum of durability depending on the material and application requirements. By understanding the strengths of various materials and considering environmental factors, you can choose the perfect heat shrinkable tube to ensure long-lasting protection and performance in your project. Remember, the most durable heat shrinkable tube is the one that best suits the specific demands of your application.


 English
English  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик